Shenzhen’s Industrial Robots Transforming Manufacturing Lines
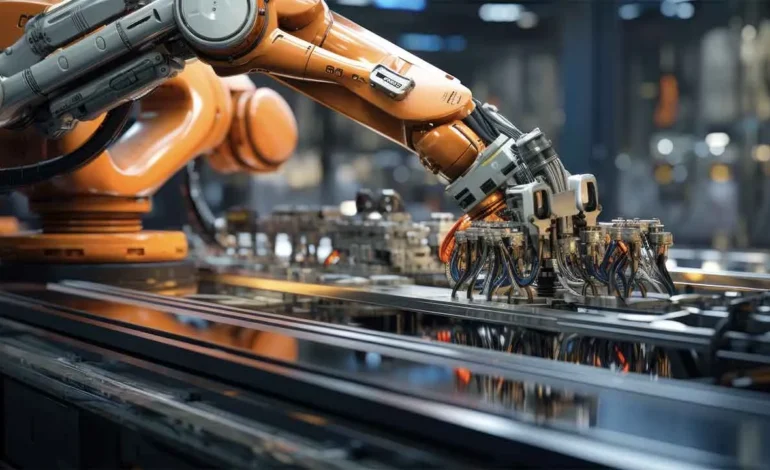
Shenzhen, often called China’s Silicon Valley, is now becoming the global capital of industrial robotics. Once a center for electronics assembly, the city has evolved into a hub where intelligent manufacturing meets automation. The rapid adoption of industrial robots is reshaping how factories operate, boosting efficiency, quality, and global competitiveness. Supported by strong government incentives and a dynamic ecosystem of startups, Shenzhen’s robotics revolution is setting a blueprint for the rest of the country. As automation replaces manual processes, China’s manufacturing sector is moving closer to its long-term goal of smart, self-optimizing production.
From Assembly Lines to Smart Factories
Factories across Shenzhen are transitioning from labor-intensive operations to highly automated production systems. Robotics integration is no longer limited to large corporations; small and medium enterprises are also investing in collaborative robots, or cobots, to handle repetitive tasks. These machines perform precision assembly, welding, packaging, and inspection at speeds unattainable by humans. At Foxconn’s manufacturing plants, for example, hundreds of robotic arms assemble components for smartphones and consumer electronics. The result is consistent output, reduced error rates, and increased operational efficiency. Automation also allows companies to manage rising labor costs while maintaining global price competitiveness.
Government Policy and Strategic Vision
The local government plays a crucial role in promoting automation through its “Shenzhen Manufacturing 2025” plan. This initiative encourages industries to adopt smart machinery and develop indigenous technologies rather than rely on imported equipment. Subsidies and tax credits support companies investing in robotics research, while dedicated industrial parks such as the Shenzhen Robotics Industrial Zone provide research facilities, testing centers, and access to venture funding. This public-private partnership model ensures continuous innovation and rapid deployment of automation technologies across diverse sectors including electronics, automotive, and logistics.
The Rise of Domestic Robotics Champions
Shenzhen is home to several emerging robotics giants that are reshaping the industry landscape. Companies like DJI, Han’s Laser, and Inovance Technology are extending their expertise beyond consumer products into industrial automation. DJI, known globally for drones, is now developing robotic platforms for warehouse logistics and factory inspections. Han’s Laser specializes in robotic welding and precision cutting systems used in automotive manufacturing. Inovance Technology provides motion control components that power thousands of industrial robots nationwide. The collaboration among these firms reflects a new phase of vertical integration where robotics, AI, and sensors form a unified ecosystem.
AI and Machine Vision Integration
Modern industrial robots in Shenzhen rely heavily on artificial intelligence and machine vision to perform complex tasks. High-resolution cameras combined with deep learning algorithms enable robots to identify components, detect defects, and adjust operations autonomously. This technology is particularly valuable in semiconductor assembly, where precision must reach micron-level accuracy. Machine vision also enhances safety, allowing cobots to work alongside humans without physical barriers. As AI models become more efficient, robots can adapt to production changes in real time, ensuring continuous productivity. The integration of AI transforms robotics from static automation into dynamic intelligence.
Startups and Innovation Ecosystem
Beyond established companies, Shenzhen hosts hundreds of robotics startups specializing in hardware design, software control, and industrial applications. Accelerators such as HAX and Shenzhen Robotics Lab nurture early-stage companies with mentorship, funding, and global exposure. These startups are exploring innovations in soft robotics, autonomous logistics, and flexible manufacturing systems. The city’s proximity to component suppliers and electronics manufacturers gives startups a unique advantage in rapid prototyping and cost-effective scaling. This ecosystem fosters competition and collaboration simultaneously, creating a fertile ground for continuous technological advancement.
Workforce Transformation and Skill Development
Automation is changing the skill profile of Shenzhen’s workforce. While repetitive jobs are declining, demand for technicians, engineers, and AI specialists is rising. The government and private sector have launched joint training programs to reskill workers for smart manufacturing. Institutes like Shenzhen Polytechnic and Southern University of Science and Technology offer courses in robotics engineering, automation control, and industrial data analytics. These initiatives ensure that human talent keeps pace with technological progress. The transition highlights how automation, rather than eliminating jobs entirely, is redefining them toward higher-value tasks that require human judgment and creativity.
Global Competitiveness and Export Growth
Shenzhen’s robotics industry is gaining traction in international markets. Exports of industrial robots and automation systems have increased by more than 40 percent year-on-year. Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe are emerging as key export destinations where Chinese robotic systems are valued for their cost-effectiveness and adaptability. The city’s robotics firms are participating in global trade fairs such as Automatica and Hannover Messe to showcase their technology. As manufacturing nations worldwide seek affordable automation, Shenzhen’s robots offer a balance between performance and price. This growing global footprint solidifies China’s role as a supplier of advanced manufacturing solutions.
Environmental and Economic Efficiency
Automation also contributes to sustainability. Robots minimize material waste, reduce energy consumption, and enable precise manufacturing that lowers defect rates. Factories adopting robotics report improvements in resource utilization and a reduction in carbon emissions. In addition, predictive maintenance powered by AI ensures machines operate efficiently and with minimal downtime. These efficiencies translate into lower costs and improved environmental performance. The alignment between economic efficiency and sustainability reinforces Shenzhen’s reputation as a model for green manufacturing innovation.
Challenges and Industry Maturity
Despite rapid growth, the robotics sector faces challenges. Supply chain dependencies, particularly for high-precision sensors and chips, remain a concern. Some smaller factories struggle with the upfront cost of automation and the lack of technical expertise for maintenance. To address these gaps, financial institutions in Shenzhen are offering robotics leasing programs and shared service models that allow companies to adopt automation without heavy capital investment. Industry associations are also establishing standardization frameworks to ensure interoperability between systems. As these measures take effect, the industry is expected to mature and scale even faster.
Future Outlook
By 2025, Shenzhen’s industrial robotics market is projected to exceed 20 billion dollars in value. The city’s factories are expected to achieve near-total automation in key sectors such as consumer electronics, textiles, and automotive components. The combination of local innovation, policy support, and global demand positions Shenzhen as a pioneer in the future of smart manufacturing. The ongoing convergence of robotics, AI, and digital infrastructure will continue to drive productivity and redefine global supply chains. What began as an experiment in automation is now a structural transformation of China’s industrial economy.
Conclusion
Shenzhen’s robotics revolution demonstrates how strategic planning and technological innovation can transform an entire manufacturing landscape. By merging automation with artificial intelligence and advanced materials, the city has turned industrial robotics into a symbol of China’s next economic chapter. As factories evolve into smart production centers, Shenzhen’s success offers a preview of the future where machines and humans collaborate to build the foundations of global industry.



