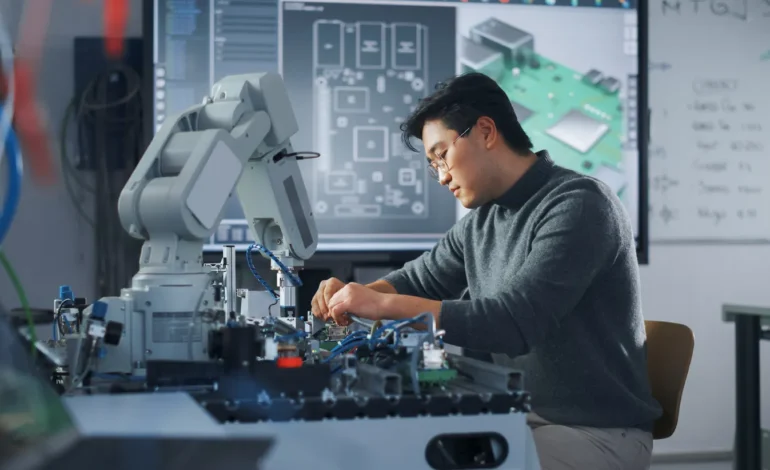
Shenzhen’s Industrial Robots Achieve Full Smart-Factory Integration

Shenzhen has reached a major milestone in China’s industrial automation drive as local factories achieve complete smart-factory integration powered by artificial intelligence, robotics, and data-driven management systems. The transformation, guided by national policy incentives and rapid private-sector innovation, positions Shenzhen as a global benchmark for intelligent manufacturing and digital supply chain optimization.
From Assembly Lines to Autonomous Systems
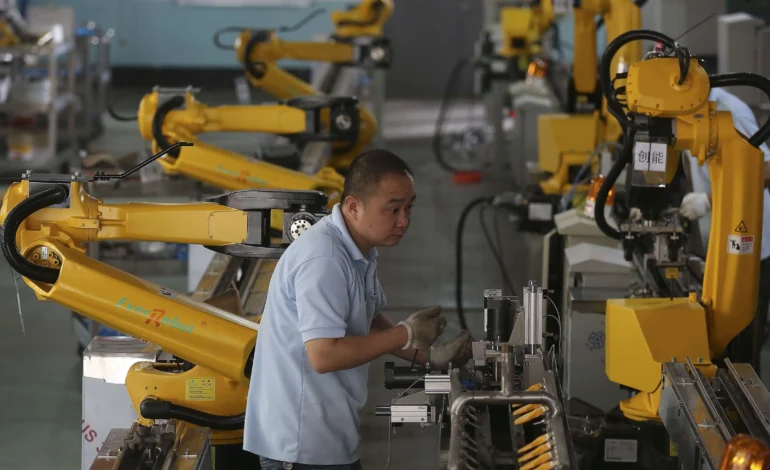
Over the past decade, Shenzhen has evolved from an electronics manufacturing hub into a testing ground for fully automated production systems. Factories now operate with interconnected robots capable of real-time communication, dynamic scheduling, and predictive maintenance. Industrial arms equipped with advanced sensors and AI algorithms adjust speed and precision automatically based on production requirements. This transition from semi-automation to full autonomy has improved productivity by nearly 30 percent and reduced error rates across high-volume sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive parts, and precision instruments.
Government Policy and Industrial Incentives
The success of Shenzhen’s automation program reflects a coordinated policy framework combining tax incentives, R&D funding, and talent development. The city government’s “Robot Plus” initiative offers subsidies to companies adopting smart manufacturing solutions. In parallel, national policy under the 14th Five-Year Plan prioritizes intelligent manufacturing as a key driver of economic modernization. The collaboration between municipal and central authorities ensures that Shenzhen’s factories receive consistent regulatory support, stable energy supply, and high-speed connectivity, creating ideal conditions for scaling automation across industries.
AI-Driven Production and Data Intelligence
Artificial intelligence plays a critical role in optimizing every layer of the production process. Machine learning models forecast component demand, analyze energy efficiency, and detect quality anomalies before they impact output. Cloud-based platforms aggregate data from hundreds of robotic units, enabling managers to adjust workflows remotely through digital control panels. Predictive analytics improve decision-making by identifying patterns in material use, equipment wear, and consumer demand. This fusion of AI and robotics is transforming traditional manufacturing into an adaptive ecosystem capable of self-improvement through continuous learning.
Collaborative Robots and Workforce Evolution
The new industrial model does not eliminate human participation but redefines it. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside technicians to perform tasks requiring flexibility, safety awareness, or fine-tuned manual adjustments. Workers now focus on system design, data analysis, and process supervision rather than repetitive labor. Shenzhen’s vocational institutes have introduced specialized programs in robotics engineering, industrial AI, and digital factory management. This human–machine synergy is fostering a new generation of skilled workers equipped to manage intelligent industrial environments.
Supply Chain Connectivity and Efficiency
Smart-factory integration in Shenzhen extends beyond production floors into logistics and supply chain management. Real-time communication between factories, suppliers, and distributors enables seamless coordination of raw materials and finished goods. Autonomous guided vehicles transport materials across facilities, while AI-driven inventory systems predict shortages and automatically place orders. These interconnected networks significantly reduce lead times and improve delivery reliability, strengthening Shenzhen’s role as a global export hub for intelligent products.
Sustainability and Energy Optimization
Automation is also driving sustainability across Shenzhen’s industrial zones. Energy management systems powered by AI monitor machine performance and automatically regulate electricity consumption. Factories use digital-twin technology to simulate production scenarios that minimize waste and optimize resource use. Green manufacturing standards introduced by local authorities require real-time reporting of emissions and recycling rates. The integration of robotics and environmental monitoring supports Shenzhen’s ambition to become a carbon-efficient industrial ecosystem by 2030.
Global Influence and Future Expansion
Shenzhen’s success is influencing manufacturing strategies across Asia, Europe, and Latin America. International delegations visit the city to study its model for integrating robotics, AI, and digital management into cohesive industrial ecosystems. Chinese technology firms are exporting turnkey smart-factory solutions to global partners seeking efficiency and sustainability. Analysts predict that Shenzhen’s share of high-value automated exports will continue to grow, reinforcing its reputation as the world’s most advanced industrial innovation zone. The city’s achievements demonstrate how digital intelligence and policy coordination can redefine manufacturing for a new technological era.