Cobots and AI Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency Across Provinces
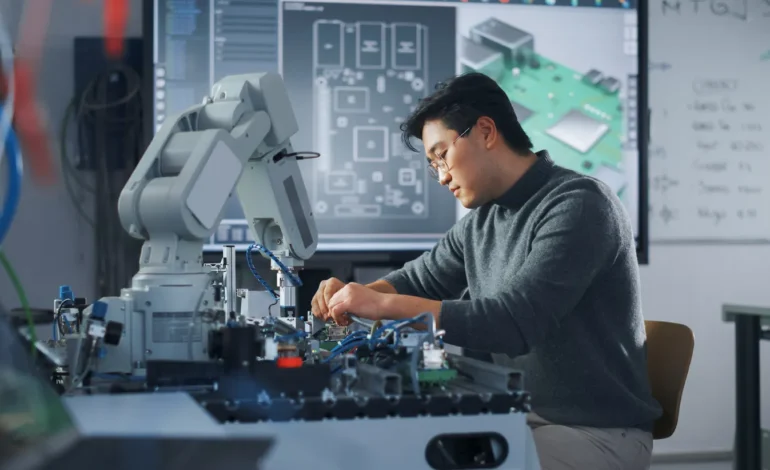
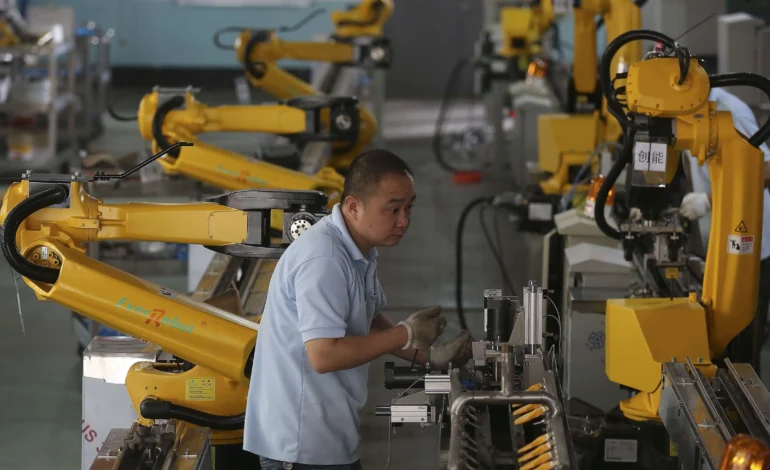
China’s industrial modernization is accelerating as collaborative robots and artificial intelligence reshape manufacturing across multiple provinces. Once limited to high-end electronics and automotive factories, cobots, robots designed to work safely alongside humans, are now being deployed across medium and small enterprises in sectors ranging from textiles to pharmaceuticals. The integration of AI into these systems is enhancing productivity, flexibility, and sustainability, establishing a new standard for smart manufacturing in the post-industrial era.
The Expansion of Collaborative Robotics
Collaborative robotics adoption is spreading rapidly beyond coastal innovation hubs like Shenzhen and Shanghai into inland provinces such as Henan, Hubei, and Sichuan. These regions, traditionally dependent on manual assembly and labor-intensive industries, are embracing cobots to offset rising labor costs and improve production consistency. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has launched regional grants to support the deployment of robotic systems in local factories. The goal is to bridge the technological gap between urban and interior regions, creating a unified national framework for intelligent industrialization.
Human–Machine Synergy in Modern Factories
Unlike conventional industrial robots that operate in isolation, cobots are designed for collaboration. Equipped with advanced sensors, machine vision, and force control systems, they can adjust their movements in response to human proximity. Workers and robots now share production spaces where human creativity complements robotic precision. In automotive parts factories in Hunan and Jiangsu, cobots handle repetitive welding and assembly tasks while technicians oversee calibration and maintenance. This hybrid workflow improves safety and productivity, reducing downtime while enhancing overall output quality.
AI-Driven Optimization and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence provides the decision-making intelligence behind modern cobot systems. Through continuous learning, AI algorithms analyze production data to identify bottlenecks, forecast maintenance needs, and optimize scheduling. Cloud-based monitoring platforms gather real-time performance data from thousands of machines, allowing remote engineers to fine-tune production across multiple facilities. This predictive capability prevents equipment failures and minimizes energy waste. The convergence of AI and collaborative robotics transforms static assembly lines into adaptive, data-driven ecosystems capable of self-correction and continuous improvement.
Empowering Small and Medium Enterprises
China’s industrial policy now focuses on equipping small and medium enterprises with affordable automation tools. Modular cobot systems are designed for easy integration into existing facilities without large-scale reconfiguration. Local robotics startups are offering subscription-based automation services that include AI-driven analytics and on-site support. These models lower entry barriers for smaller manufacturers, enabling them to compete with larger enterprises in quality, speed, and efficiency. By democratizing access to automation, China is building a more balanced and resilient industrial base.
Education and Workforce Transformation
The expansion of cobots and AI is reshaping the nature of industrial employment. Technical schools and vocational training centers across provinces are introducing new programs in robotics maintenance, AI programming, and smart-factory operations. Workers are transitioning from manual assembly to data supervision and process management roles. This shift improves job quality while ensuring that human expertise remains central to industrial innovation. The focus on workforce transformation supports China’s long-term goal of developing a skilled, adaptable labor force capable of managing intelligent industrial systems.
Regional Competitiveness and Economic Growth
The spread of cobot technology contributes directly to regional economic revitalization. In Chengdu, smart robotics clusters have boosted manufacturing output by 15 percent in less than two years. In Wuhan, AI-assisted robotic assembly lines have shortened production cycles in the electronics sector by nearly 40 percent. These efficiency gains attract foreign investment and create new ecosystems of suppliers, logistics firms, and software developers. The integration of AI and robotics across provinces is driving an industrial upgrade that supports both national competitiveness and local economic resilience.
Nationwide Smart Manufacturing Network
China’s cobot revolution is creating a unified digital manufacturing network where data flows seamlessly between factories, suppliers, and regulators. Cloud platforms connect regional production hubs, allowing standardized performance benchmarking and quality assurance. As 5G connectivity expands, real-time collaboration between human workers and cobots will become even more efficient, enabling instant decision-making across vast industrial chains. This interconnected model demonstrates how China’s multi-provincial automation drive is evolving from isolated innovation to a cohesive, nationwide transformation in intelligent manufacturing.



