Autonomous Vehicle Development and Pilot Cities
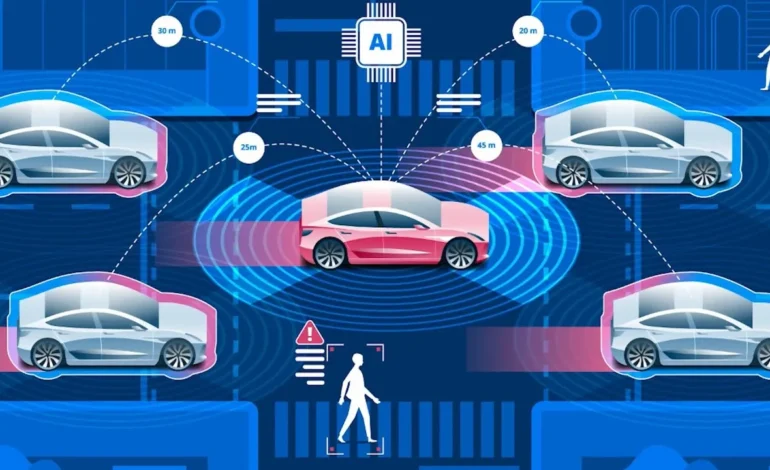
China has emerged as a global leader in autonomous vehicle (AV) research and development, leveraging government support, technological innovation, and urban pilot programs. By 2025, AV development is accelerating rapidly, with multiple pilot cities testing advanced autonomous mobility solutions. These initiatives are aimed at improving traffic safety, reducing congestion, and creating smart city ecosystems. Autonomous vehicle technology in China spans multiple layers, including perception systems, AI-driven decision-making, connected infrastructure, and regulatory frameworks. This blog explores the current state of AV development, the role of pilot cities, technological innovations, and implications for urban mobility.
Government Policies and Regulatory Support
Government policies are instrumental in shaping China’s AV ecosystem. The Ministry of Transport and local municipal authorities have introduced guidelines for testing, data collection, and road safety compliance. Pilot city programs provide controlled environments for testing autonomous shuttles, taxis, and logistics vehicles. These policies also encourage public-private partnerships, enabling technology firms, OEMs, and mobility operators to collaborate on deployment strategies while ensuring safety and regulatory adherence.
Technological Advancements in AV Systems
China’s AV development focuses on key technologies, including LiDAR, radar, high-definition maps, and AI-based perception algorithms. Advanced sensors enable vehicles to detect obstacles, pedestrians, and other road users with high accuracy. AI systems process this data to make real-time navigation and driving decisions. Connectivity solutions such as 5G and V2X communication allow vehicles to interact with traffic signals, other vehicles, and infrastructure, enhancing safety and traffic efficiency. Integration of these technologies supports both fully and partially autonomous vehicle operations.
Pilot Cities and Testing Programs
Several Chinese cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, serve as AV pilot hubs. These cities provide dedicated testing zones, smart traffic management systems, and data collection platforms. Pilot programs involve a combination of autonomous taxis, delivery vehicles, and public transport shuttles. These initiatives allow developers to refine software algorithms, validate sensor performance, and optimize fleet operations. Pilot city programs also facilitate regulatory learning, helping authorities establish frameworks for large-scale AV deployment.
Industry Collaboration and Ecosystem Development
Collaboration between automotive manufacturers, tech companies, and research institutions accelerates AV development. Companies such as Baidu, Pony.ai, AutoX, and NIO are partnering with city authorities to deploy autonomous fleets. These collaborations focus on mapping, AI training, fleet management software, and edge computing infrastructure. By integrating expertise from multiple sectors, China is creating a robust AV ecosystem capable of supporting safe and efficient urban mobility.
Impact on Urban Mobility
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform urban transportation. AVs can reduce traffic congestion through optimized routing, improve road safety by minimizing human error, and enhance mobility accessibility for elderly and disabled populations. Integration with ride-hailing platforms and public transit systems supports multimodal transportation networks. In pilot cities, AV deployment provides insights into traffic flow management, infrastructure planning, and environmental impact, contributing to smarter, greener cities.
Challenges and Safety Considerations
Despite rapid progress, challenges remain. Sensor limitations in adverse weather, ethical decision-making algorithms, cybersecurity risks, and public acceptance are critical issues. Pilot programs are essential for identifying these challenges and testing solutions in real-world environments. Government oversight, industry standards, and ongoing research are crucial to ensuring safe and reliable autonomous vehicle operations.
Future Outlook
By 2025, autonomous vehicle technology in China is moving from experimental testing to commercial deployment. Expansion into tier-2 and tier-3 cities, integration with smart city infrastructure, and improvements in AI perception and control systems are expected. Regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to accommodate larger-scale AV operations, enabling safer, more efficient, and environmentally sustainable urban mobility.
Conclusion
China’s autonomous vehicle development in 2025 demonstrates significant technological innovation, strategic pilot programs, and strong government support. Pilot cities serve as testing grounds for refining AV systems, integrating AI and connectivity, and preparing for large-scale deployment. As AV technology matures, it promises to reshape urban mobility, enhance safety, and contribute to the development of smart, sustainable cities across China.



